Albert Einstein's quote, "If the bee disappears from the surface of the Earth, man would have no more than four years left to live" is one of the most widely used statements that emphasizes the important role bees play in human life.
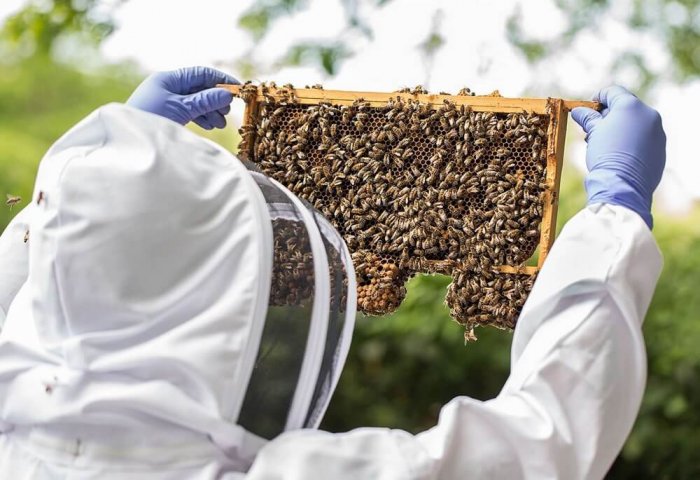
In addition to producing some products (honey, beeswax, royal jelly, pollen, propolis), bees contribute to the reproduction of plants and food products by means of pollination. As such, bees, being some of the most industrious creatures in the world, have been benefiting people, plants, and the environment for centuries.
Bees and other pollinators, by carrying pollen from one flower to another, ensure not only the productivity of fruits and plants, but also their diversity and high quality. Pollinators such as bees, birds and bats have a direct impact on 35% of global fruit production.
Beekeeping is a global sector that is a source of livelihood for millions of beekeepers. Bees play an important role in conserving biodiversity, supporting reforestation, resilience and adaptation to climate change, and ensuring the vitality and reproduction of plants and increasing the quantity and quality of agricultural products.
Bees not only contribute to plant pollination, but also play an important role in protecting floral biodiversity within the scope of the Sustainable Development Goals. The existence of bee colonies can be affected by pesticides. In 2017, the United Nations declared May 20 each year as World Bee Day to raise awareness of the important role of bees and their contribution to sustainable development, as well as the dangers they face.
Beekeeping should not only be seen as an important activity for the pollination of plants. Given the sales of bee products and their health benefits, it also generates added value for the economy.
The best-known beekeeping product is honey. According to the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), 1.861 million tons of honey were produced worldwide in 2017. But global revenues from honey account for only 25% of total revenues from the beekeeping sector. In addition to honey, bee products such as beeswax, bee milk and pollen are also in high demand.
In addition, in developed countries such as the U.S. and Russia, beekeeping is carried out in order to increase the quantity and quality of plant production together with the production of bee products.
In the U.S., for example, crop growers pay an average of $41 million a year to "rent" bees to provide pollination for their plants, which in turn contributes to an average of $3.2 billion a year of income for them.
Another U.S. study found that about one-third of the $30 billion in total income from the production of about 40 types of crops, i.e. about $10 billion, was provided by bees.
The history of beekeeping in Turkmenistan dates back to ancient times. Mobile beekeeping is widespread in the country. In the spring, honey is harvested from different desert plants in the Garagum Desert. In Turkmenistan honey is mainly collected from such plants as yandak (camel's thorn), cotton and clover. Honey production in cotton fields helps to increase the crop yield by 25-30%.
Turkmen beekeepers can increase honey yield and quality by adopting and using new techniques in beekeeping. At the same time, they have an opportunity to produce not only honey, but also other products such as bee venom, beeswax, and royal jelly, tapping into significant revenue streams in world markets.
Nurmyrat Mommayev,
PhD Candidate at Marmara University's Department of Political Science and International Relations in Istanbul, Turkey