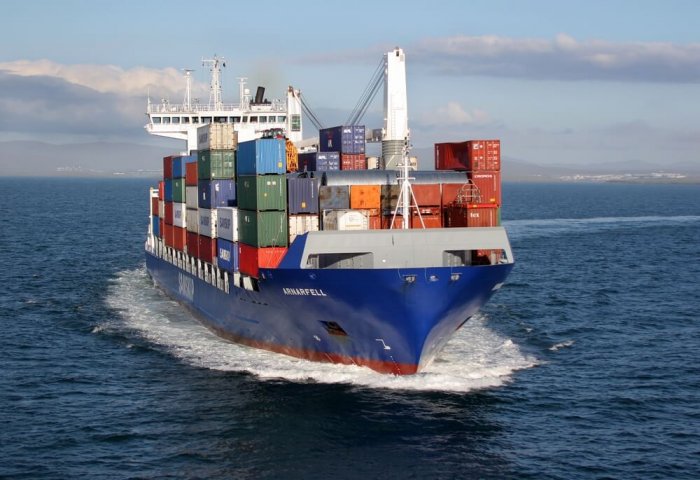
Foreign trade is the purchase and sale of goods and services made by a country beyond its borders. Due to the greater globalization of the world in recent years, foreign trade has an impact not only on the economy of a country, but also on the economy of all countries that work together for economic benefits.
Foreign trade also uses a number of terms in purchase and delivery of goods. The International Chamber of Commerce publishes a series of pre-defined commercial terms – International Commercial Terms or Incoterms.
These incoterms are also used in the auctions held at the State Commodity and Raw Materials Exchange of Turkmenistan that are daily published by Business Turkmenistan. Incoterms inform sales contracts defining respective obligations, costs, and risks involved in the delivery of goods from the seller to the buyer.
The following three incoterms are widely used in Turkmenistan:
EXW – Ex Works
This term means that the Seller fulfills his obligations under a foreign trade contract when he makes the products available for the Buyer directly at his enterprise, i.e. warehouse or enterprise. The Seller is not responsible for loading or unloading the goods on the transport vehicle of the buyer, if not provided. The Buyer is responsible for all costs associated with the delivery of goods from the factory or warehouse of the seller. This term places the maximum obligation on the Buyer and minimum obligations on the Seller.
The EXW sale price includes only the price of the packaged goods. In other words, from the moment of delivery of the goods at the Seller’s premise, all types of transport, handling and insurance costs are paid by the Buyer.
FCA – Free Carrier
In this case, the seller's obligations are fulfilled when the goods, cleared for export, are delivered to the carrier or destination specified by the Buyer.
If the Buyer has not indicated a specific place of delivery of the goods, then the Seller himself can deliver the goods to the place where the carrier can come and pick it up. If the transaction requires the seller's assistance to conclude a contract with the carrier (for example, in rail and air transport), the seller may act at the buyer's risk and expense.
FOB – Free on Board:
In this case, the Seller's obligation are fulfilled when the goods are delivered on board the ship and are cleared for export. From that point, the Buyer bears all costs and risks of loss or damage.
Nurmyrat Mommayev,
PhD Candidate at Marmara University's Department of Political Science and International Relations in Istanbul, Turkey